Calterah mmWave Radar Application for Indoor Detection and Tracking of Human Body
The application of millimeter wave (mmWave) radar technology for indoor detection and tracking of the human body has just been emerging in recent years. The underlying principle is that electromagnetic wave signals emitted through radar antenna shall be reflected after being blocked by objects on its emitting path and be received by the radar receiving antenna, so that through a series of processing of the received signals, the distance, velocity, and angle information of the object can be obtained.
At present, besides mmWave radar, ultrasonic sensors, passive infrared sensors, active infrared sensors (such as LiDAR and ToF), and optical cameras are also used for indoor detection and tracking of the human body. However, these sensors can be easily affected by external environment conditions (for example, light, temperature, etc.), causing false alarms. By contrast, mmWave radar can operate stably and reliably 24/7 under all-weather conditions, demonstrating superior performance in meeting the requirements of indoor detection and tracking of the human body. That’s why mmWave radar is more and more widely used in security monitoring, smart home, smart elderly care, automatic door control, and other fields. When it comes to personal privacy, in particular, mmWave radar has irreplaceable advantages against others.
Calterah mmWave radar application for indoor detection and tracking of the human body is developed based on Calterah 60GHz and 77GHz mm-Wave radar chip families, employing FMCW and MIMO technologies. With high accuracy in range and velocity, high angular resolution, and low false alarm rate, the application is capable of detecting, positioning, and tracking people in a precise and reliable manner in indoor environments. It can effectively distinguish humans from other objects, count the number of the people indoors, and output their range, velocity, and angle information stably. Figure 1 demonstrates the performance of Calterah mmWave radar sensor for indoor detection and tracking of the human body. The radar sensor excludes static objects like tables, chairs, and walls, and achieves accurate detection and positioning and stable tracking of three people indoors at the same time.
Figure 1 A demo of Calterah mm-Wave radar sensor detecting and tracking the human body in an indoor environment
Calterah mmWave radar application for indoor detection and tracking of the human body employs FMCW and MIMO technologies and utilizes key algorithms such as static clutter cancellation, multipath interference cancellation, group-target tracking, and human and non-human object classification, so as to tackle false targets brought about by indoor multiple paths and effectively classify human and other objects, realizing the function of tracking and positioning multiple targets in indoor environments.
The static clutter cancellation algorithm is mainly used for eliminating static objects (for example, walls, tables, chairs, etc.) in indoor environments. Applied in both the signal processing module and the data processing module, the algorithm filters out the static objects by eliminating targets in the zero Doppler channel, avoiding the interference with the detection of moving targets from the static objects.
The multipath interference cancellation algorithm is mainly used for eliminating false detection points brought about by the motion of targets in indoor scenes, avoiding the possibility that the false detection points are mistaken for the targets by the mmWave radar sensor and thus tracked and output, causing false alarms, as shown in Figure 2. The algorithm makes a comprehensive judgment, according to the area of the indoor environment and the information of an original detection point obtained by the mmWave radar sensor (such as range, velocity, angle, and signal-to-noise ratio), to determine whether the original detection point is a false point. If yes, the false point will then be filtered out, hence reducing the false alarms caused by multipath in indoor environments.
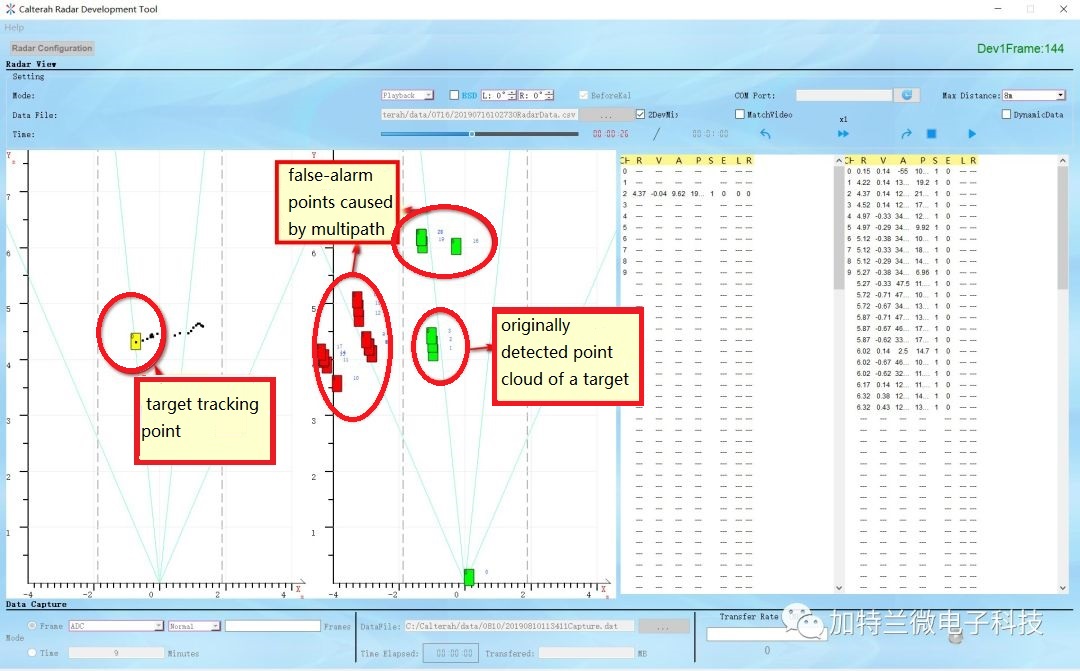
Figure 2 False detection points caused by indoor multipath
The group-target tracking algorithm is mainly used for precisely positioning and stably tracking multiple moving targets in indoor environments. The algorithm first effectively groups the original detection points to obtain different target clusters. Then, the extended Kalman filter (EKF) algorithm is utilized to achieve the tracking and filtering of different clusters, and finally get stable trails of the moving targets.
The human and non-human object classification algorithm is mainly used for distinguishing humans from slightly moving objects (for example, spinning fans, fluttering curtains, etc.) Such an object has a certain Doppler velocity, which can be mistakenly tracked and output by the mmWave radar sensor. By summing up and extracting the features of humans and slightly moving objects, the human and non-human object classification algorithm can classify targets and output only the tracking results of humans.
In the future, Calterah mmWave sensors will be enhanced by adding the feature of recognition of human posture, based on the current application for indoor detection and tracking of the human body, so as to realize accurate detection and positioning, stable tracking, and intelligent recognition of the human body, contributing to a safer and smarter social environment.
